Using Variables
This topic describes the types of variables you can define when creating models. Variables are placeholders that you could use to store values. They can be numbers, text, or values such as true or false. There are three types of variables in Eggplant AI that are described below: State variables, Action variables, and Global variables.
State Variables
State variables can be used in a specific state as well as an action within a state. It can also be passed in and out of a snippets called by that state.
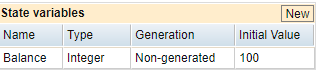
To add a new state variable, click New in the State variables section. You can also select then right-click the state in the Model tab, then select New Variable from the context menu. Then, configure state variables by using the following selections:
- Name: Enter an appropriate name for your variable. You can use all Unicode characters but double quotes in this field.
-
Type: Enter the appropriate variable type from the drop-down menu:
- Integer: This selection defines a variable as a whole number (not a fraction) that can be positive, negative, or zero. Use the integer variable type in models when, for instance, a count of something is important, such as the number of users or test cases.
- True or False: Use this data type when your model requires a Boolean value such as on or off, true or false, and other similar values.
- Real: The real data type includes rational numbers, such as 5, -5, and 2/3. It also includes irrational numbers, such as the square root of 2. Use a real data type for values such as for degrees, radians, or other similar information.
- Text: Use this data type for storing a string or to define an allowable list of characters as a string. It can be any integer constraint, i.e., 2, 4, 8, 16 would make a string of either 2, 4, 8, or 16 characters long and much like other constraints, you can combine multiple constraints here. If you want to set a range of allowable characters, you must make them a range, e.g., 'a':'z' or a list "aeiou". Remember that the single and double quotes are important.
- Set: This selection lets you define a set of allowed values for this variable. Use this selection if you want Eggplant AI to select a value from a specific list of values at runtime. For example: 'spring', 'summer', 'autumn', 'winter’. To input your list of values, right-click the variable, select Edit Variable Details from the context menu, then use the Values section of the Variable Properties dialog box to set the values. You can use all Unicode characters but double quotes in this field.
- Record: This selection lets Eggplant AI read variable values from records contained in a CSV file. Go to File > Manage Execution Environments to identify the directory containing the CSV files. When Eggplant AI accesses this variable, it selects one of the records from the CSV file and stores it in the variable.
-
Generation: Enter the appropriate variable generation method from the drop-down menu:
- Generated: Generates a new value for a variable based on its variable type.
- Generated Unique: Generates a value but can't reuse a value that has been previously used.
- Generated one-time: The generated value is selected once and then not selected again. The value remains static throughout the run.
- Non-generated: The value is not generated and must be set to contain a value.
- Initial Value: Set the initial value, if any, for this variable. When using variables of the type Record, the option you select in the Initial value field will determine the .csv file from where the records should be read from.
To edit an existing variable, select it and update the information in the State variables section. To further customize variables, right-click the variable, then select Edit Variable Details. The Variable Properties dialog box lets you set an initial value as well as value ranges and other details.
To remove a variable, right-click the variable in the State Variables section, then select Remove Variable from the context menu.
Action Variables
Action variables capture and provide values for states and actions. To add a variable to an action, right-click the action, then select New Variable in the drop-down menu. You can also select an action, then click New in Action variables, located in the right pane.
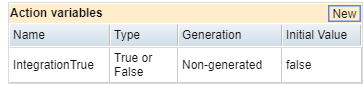
The Action Variables section of the Action Properties tab
To set the properties for generating a variable, right-click the variable, select Edit variable details in the context menu, then use the Variable properties dialog box to set the criteria.
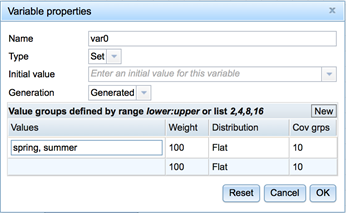
- Name the variable. You can use all Unicode characters but double quotes in this field.
-
Select a variable Type:
- Integer: This selection defines a variable as a whole number (not a fraction) that can be positive, negative, or zero. Use the integer variable type in models when, for instance, a count of something is important, such as the number of users or test cases.
- True or False: Use this type when your model requires a Boolean value, such as on or off, true or false, or similar values.
- Real: The real data type includes rational numbers, such as 5, -5, and 2/3. It also includes irrational numbers, such as the square root of 2. Use a real data type for values such as for degrees, radians, or other similar information.
- Text: Use this data type to store a string. You can also use the Text data type to define an allowable list of characters as a string. You can use all Unicode characters but double quotes in this field.
- Set: This selection lets you define a set of allowed values for this variable. Use this selection if you want Eggplant AI to select a value from a specific list of values at runtime. For example: 'spring', 'summer', 'autumn', 'winter’. To input your list of values, right-click the variable, select Edit Variable Details from the context menu, then use the Values section of the Variable Properties dialog box to set the values. You can use all Unicode characters but double quotes in this field.
- Record: This selection lets Eggplant AI read variable values from records contained in a CSV file. Go to File > Manage Execution Environments to identify the directory containing the CSV files. When Eggplant AI accesses this variable, it selects one of the records from the CSV file and stores it in the variable.
Note: When using data from a CSV file to pass values to a variable, if a row of the CSV file contains four comma separated values (e.g., "spring, summer, autumn, winter"), then the whole row will be passed to the variable. If you only require a specific value from the list, e.g., "autumn", then you must parse it using a snippet in Eggplant Functional.
- Set the Initial value of the variable. When using variables of the type Record, the option you select in the Initial value field will determine the .csv file from where the records should be read from.
-
Set the Generation method you want Eggplant AI to use:
- Generated: Generates a new value for a variable based on its variable type.
- Generated Unique: Generates a value but can't reuse a value that has been previously used.
- Generated one-time: The generated value is selected once and then not selected again. The value remains static throughout the run.
- Non-generated: The value is not generated and must be set to contain a value.
-
You can add Value groups to further define the variables Eggplant AI generates. Enter a value group as a value definition, using one definition per line.
-
Values: Enter the allowable values for this group entry. You can define variable values as follows:
- Enter a static value, such as 100.
- Enter a range, such as 0:100.
- Enter a list, such as 0, 2, 4, 6, 8.
- Weight: Enter the relative weight you want Eggplant AI to use when generating this variable. For example, if you want Eggplant AI to use this value group 50 percent of the time (as compared to the other value groups) when generating this variable, enter 50 in this field.
-
Distribution: Select the statistical distribution method you want Eggplant AI to use when generating this variable:
- Flat: Use a flat statistical distribution model.
- Normal: Use a normal statistical distribution model.
- Edge: Use statistical outliers.
- Cov grps: Determines the number of segments Eggplant AI uses to divide the values entries. Eggplant AI begins with a value of 10 equal segments by default, then processes the values you enter for a value group and suggests a coverage group. For example, if you enter 0:360, as a value, Eggplant AI might suggest 10 coverage groups that include 36 possible values for each coverage group to cover the value range from 0 to 360. You can manually enter a coverage group value that meets the needs for your model.
-
Global Variables
Global variables serve the same purpose as state and action variables except they can be accessed from anywhere in the model. Global variables are available to all states and actions in a model and not limited to a particular state or action. You can pass global variable as an input for a snippet.
To add a new global variable, follow these steps:
- In the Modeler UI, click anywhere on the canvas without selecting any action or state.
- Right-click and select New Variable or in the Global Properties pane that is open on the right, click New.
- Enter the variable Name, Type, Generation method, and Initial Value. The Initial Value field is only enabled for the Non-generated method.
You can edit and remove an existing Global variable in the same as way as you would for a State or Action variable.
Note: For Generated or Generated unique methods, the value is selected by the engine based on the rules in the variable definition at the start of every Action/State execution in which it is defined before the snippet execution. If it is Generated one-time method, then it is only generated once, and that value remains for the rest of the model execution.