Changing Settings in Android Gateway 5.6 and Older
You can use the settings options in Android Gateway to customize the application and to specify special circumstances for connections. Although the default settings are fine for most devices and environments, you might need to make adjustments from time to time.
Settings options are located in the Settings sidebar on the right side of the application window. Most settings are saved specific to the device selected in the Device Table section. Therefore, if you have multiple devices connected, the settings displayed in the sidebar change if you select a different device.
Settings are saved in a configuration file on the device itself. When you reattach a device, Android Gateway reads any settings customizations that are saved on the device, so you don't have to configure your connections again. The exceptions to this behavior are the choices under Global Settings, which apply to all devices and connections.
The Settings Sidebar
The Settings sidebar is divided into categories. To see the options available in a section, click the icon beside the heading or double-click the heading itself to expand the section.

Descriptions of each section and the settings available in each follow.
VNC
The options in this section specify information about the VNC connection.
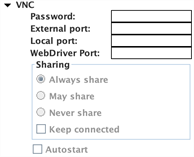
- Password: (Optional) Use this field to set a password for the VNC server on the device. You'll need to enter the same password when you create a connection from Eggplant Functional. For information about Eggplant Functional connections, see Creating Connections to SUTs.
- External port: Android Gateway uses the external port for connections with Eggplant Functional running on a different machine. The external port must be different from the local port for port forwarding to work. The default port is 5900.
Note: If you're connecting to multiple devices simultaneously, you must use a different port for each connection.
- Local port: Use this port to connect from Eggplant Functional running on the same machine as Android Gateway. Default port: 5950.
- WebDriver port: Use this port for WebDriver testing. Default port: 4723.
- Sharing: These settings determine whether or not there can be allow multiple VNC connections at the same time.
- Always share: Always allow multiple connections.
- May share: Uses the settings from the Eggplant Functional Connection Preferences tab.
- Never share: Never allow multiple connections.
- Autostart: Use this setting to have the service start automatically when you reattach the device. If this checkbox is selected, Android Gateway starts the service as soon as it recognizes the device. Not selected by default.
Reverse Connection
Use this section to set options to establish a reverse VNC connection. For instructions to make reverse connections, see Making a Reverse Connection with Android Gateway.
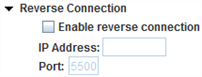
- Enable reverse connection: Select this checkbox to enable a reverse VNC connection—a connection that is initiated by the Android SUT rather than by the computer running Eggplant Functional.
- IP address: Use this field to enter the IP address of the Eggplant Functional machine when you're using a reverse VNC connection.
- Port: Use this field to set the port number over which Android Gateway communicates the reverse VNC connection. Note that Eggplant Functional must be configured to listen for reverse connections on the same port number. You can set the port in Eggplant Functional by going to Eggplant > Preferences and selecting the Connection tab. The default port is 5500.
Screen Control
Use these options to manage how the device screen is presented in Eggplant Functional.
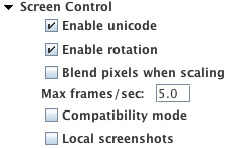
- Enable unicode: Selected by default. Allows the Unicode keyboard to work on the device.
- Enable rotation: Selected by default. Control whether or not the device's display rotates.
- Max frames/sec: This setting lets you limit the rate at which screenshots are taken on the device for drawing the remote screen. This value is specified in number of frames per second (FPS). Using a larger number of frames per second makes devices more responsive but can drain the battery even when the device is plugged into a power source. The default value is 5. Most devices are not able to take more than 5 screenshots per second.
- Blend pixels when scaling: Use this option to get better images if you're using scaling. Note that blending can cause slower performance.
- Compatibility mode: This feature is not enabled by default for most devices. This provides the best touch gesture support. However, some devices work better in compatibility mode. Some touch gestures, such as pinch and long hold, are not supported in compatibility mode.
Note: Compatibility mode is enabled by default the first time an LG G5 device is connected to Android Gateway.
- Local screenshots: Selected by default when an LG G5 device is connected to Android Gateway for the first time. Configures the SUT to allow the screenshots seen in Eggplant Functional during automation.
Advanced
This section includes advanced settings options. In most instances, you won't need to change these settings. The options on this screen are described below.
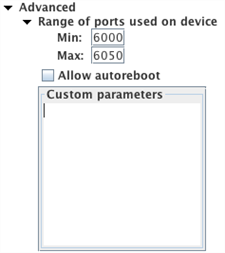
- Range of ports used on device: Android Gateway uses one port to communicate internally within the connected device. It selects the port from the port range specified in the Min and Max fields. If you have a port conflict with an app running on the phone, you can adjust the port range here.
- Allow autoreboot: Select this checkbox if you want Android Gateway to automatically reboot the device if it encounters multiple failed connections.
- Custom parameters: Enter available parameters—including those for managing things like connections, screen settings, and mouse preferences—in this field.
Note: This feature should be used only as directed by Eggplant technical support.
Logging
This section lets you make choices about the logs Android Gateway keeps.
Verbose logging: This setting enables extensive logging for debugging.
Save logs: Select this checkbox if you want to save a log file.
Global Settings
This section is where you set Android Gateway options that not device-specific.
ADB version: Use the drop-down list to select the appropriate Android Debug Bridge (ADB) version for your device. Android Gateway supports ADB versions 1.0.31, 1.0.32, 1.0.36, 1.0.39, 1.0.40, and 1.0.41. Be sure to switch the ADB version here before you connect to the Android device. The ADB version you select persists between Android Gateway sessions.
Logging directory: This field displays the path to the application home directory, which is where logs are saved if you enable that feature in the Logging section.
Privacy Settings > Share Installation Details: When this checkbox is selected, the operating system version and Android Gateway version are sent to Eggplant with each launch of Android Gateway.