Each Eggplant Functional virtual user (VU) uses an instance of Eggplant Functional to communicate with the system under test (SUT). The Eggplant Performance Injector will automatically start an instance of Eggplant Functional per VU, but in order to do this, it must know where on the injector machine Eggplant Functional is located. Also, each Eggplant Functional instance requires a different TCP port to communicate with the injector.
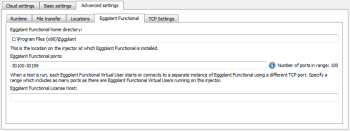
You can configure both of these options on the Advanced tab of the injector configuration in Eggplant Performance Studio:
The Eggplant Functional home directory is the location where Eggplant Functional is installed on the injector machine.
The Eggplant Functional ports is a range of TCP ports on the injector machine that can be used by Eggplant Functional instances to communicate with the injector. Each time an Eggplant Functional instance starts, the injector selects a free port from this range to use. Since the injector and Eggplant Functional are running on the same physical machine, it should not be necessary to allow any of these ports through a firewall.
Eggplant Functional Instances
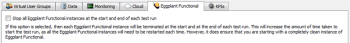
The injector will automatically detect whether an Eggplant Functional instance is running on a given port, and will only start a new instance if required. It will also leave the Eggplant Functional instance running at the end of the test run. This significantly speeds up the process of starting a test run, as Eggplant Functional can take a couple of minutes to start. However, you may prefer to stop any Eggplant Functional instances at the start and end of the test run. This guarantees that each VU in the test is using a completely "clean" instance of Eggplant Functional. This option can be found on the Eggplant Functional tab of the Test View in Eggplant Performance Studio: