Deploy Docker Desktop on Windows with WSL 2
You can deploy Eggplant Generator in a Docker Desktop container on a Microsoft Windows system with Windows Subsystem for Linux 2 (WSL 2). WSL is a Windows operating system feature that enables you to run a Linux environment on Windows without dual booting or installing another virtual machine implementation. Ubuntu is the default linux distribution type installed with WSL 2. See the Microsoft article What is the Windows Subsystem for Linux?, which includes information about WSL 2, for more information.
Deploying Docker Desktop on Windows with WSL 2 involves the following tasks:
- Verifying your system meets the minimum hardware and software requirements.
- Setting up Docker Desktop, which includes:
- Enabling virtualization on the Windows system
- Installing WSL 2 on the Windows system.
- Installing Docker Desktop
- Performing the tasks on the Eggplant Generator pre-deployment checklist
Software Requirements for Eggplant Generator with Docker on Windows
Before you can install and run Eggplant Generator in Docker Desktop on a Windows system, you need to verify your system meets the following prerequisites:
See the Prerequisites for information about the required hardware and memory for Eggplant Generator.
| Software | Version |
|---|---|
| Microsoft Windows (64-bit) |
|
| Docker Desktop | Desktop with WSL 2 enabled, up-to-date. |
| Docker Compose | Compose 2.23.0 or higher (included in the Docker Desktop bundle) |
| NVIDIA CUDA Driver | CUDA Driver for WSL, 12.x / up-to-date. See GPU in Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) for information about installing the CUDA driver. |
| Eggplant IAM (Keycloak) | See install Eggplant IAM (Keycloak). |
Deploying Docker Desktop on a Windows System
Peform the following tasks to set up Docker Desktop on the Windows system where you plan to run the Docker container that will host Eggplant Generator.
1. Enable Virtualization on the Windows System
See the Microsoft article Enable Virtualization on Windows for instructions.
2. Install WSL 2 to run a Linux environment on Windows
See the Docker article Install Docker Desktop on Windows for instructions.
3. Install Docker Desktop
-
Download the required software. Refer to the Software Requirements table above for the list of what you need.
-
Install Docker Desktop with the default settings that have
Use WSL 2 instead of Hyper-V (recommended)enabled as shown in the sample Docker Desktop installation panel below. For more information, see Install Docker Desktop on Windows in the Docker documentation.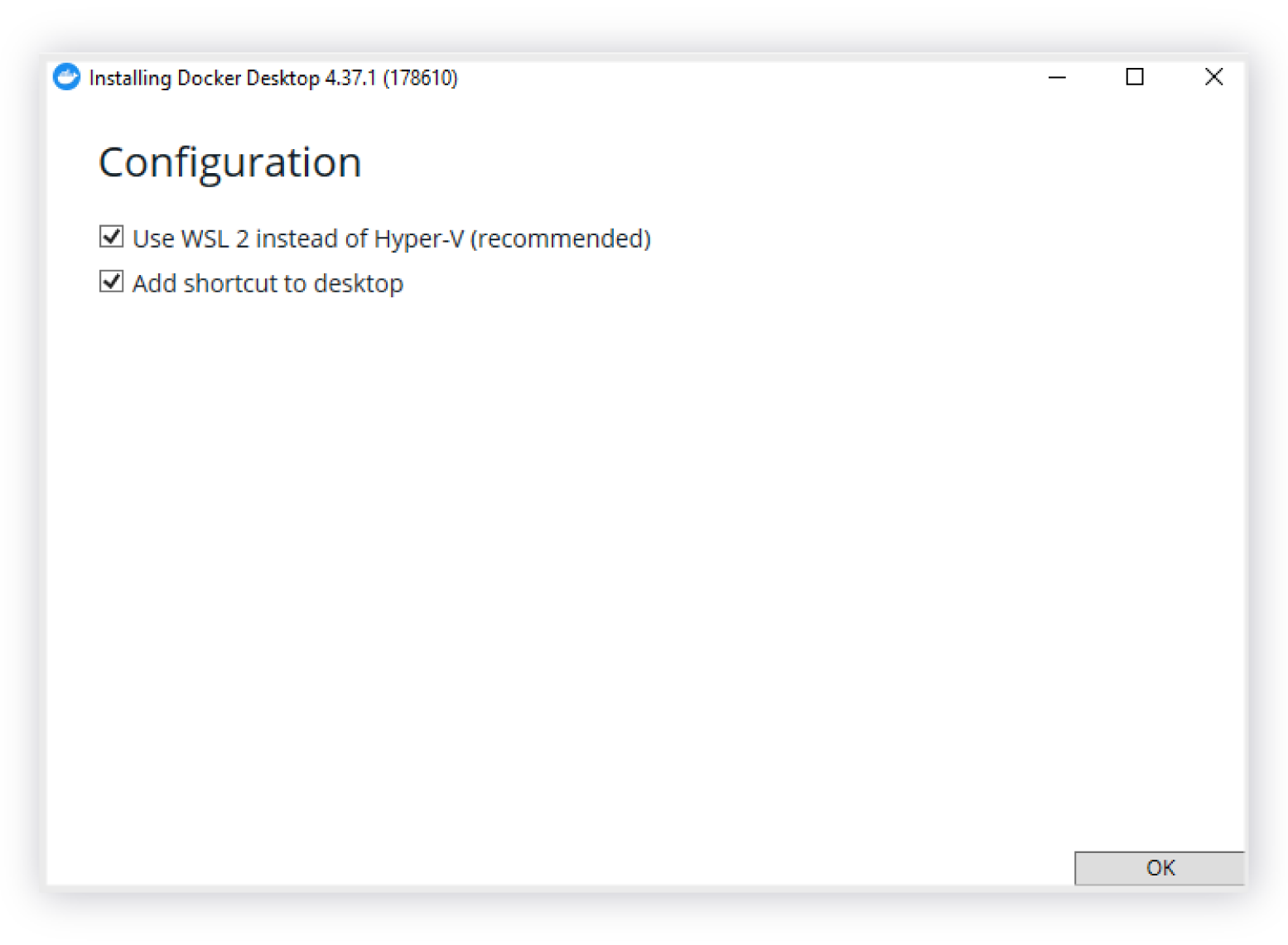 The default Use WSL 2 instead of Hyper-V (recommended) accepted during Docker Desktop installation
The default Use WSL 2 instead of Hyper-V (recommended) accepted during Docker Desktop installation -
Proceed through the installation. The Docker installation progress displays in the installer.
 The Docker Desktop installation program installing files
The Docker Desktop installation program installing files
4. Verify the Docker Desktop Deployment
This includes two tasks, instructions for which are provided below:
- Running the Docker Desktop version and
hello-worldcommands at the CLI - Verifying WSL 2 is Enabled in the Docker Desktop App
Verifying the Docker Desktop Version and Installation at the Command Line
-
Open a shell on your Windows system, if you do not already have one open.
-
Verify that the Docker Compose version is 2.23.0 or higher by running the following command in your shell. If the output from the following command shows an older version, delete the cache folder at
C:\Users\<username>\.dockerand restart Docker Desktop.docker compose version -
Verify the running the
hello-worldcommand confirms your installation is working correctly.docker run hello-worldThe resulting output should be similar to the following and include the message
your installation appears to be working correctly:Hello from Docker!
This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly.
To generate this message, Docker took the following steps:
1. The Docker client contacted the Docker daemon.
2. The Docker daemon pulled the "hello-world" image from the Docker Hub.
(arm64v8)
3. The Docker daemon created a new container from that image which runs the
executable that produces the output you are currently reading.
4. The Docker daemon streamed that output to the Docker client, which sent it
to your terminal.
To try something more ambitious, you can run an Ubuntu container with:
$ docker run -it ubuntu bash
Share images, automate workflows, and more with a free Docker ID:
https://hub.docker.com/
For more examples and ideas, visit:
https://docs.docker.com/get-started/
Verifying WSL 2 is Enabled in the Docker Desktop App
-
In the Docker Desktop app, verify that WSL 2 is enabled in the Settings, under Resources > Advanced as shown in the following sample Docker Desktop screen.
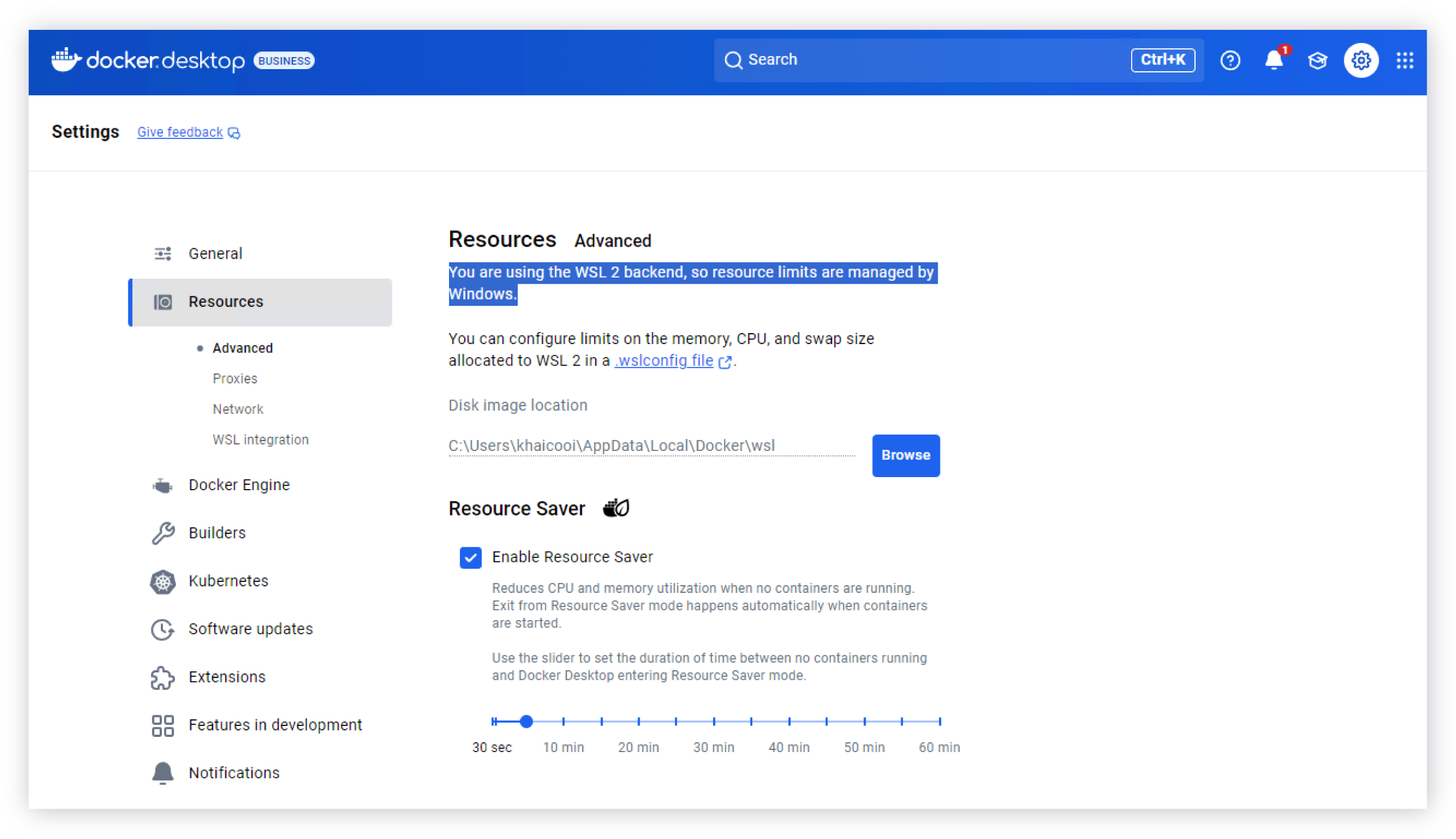 Verifying that WSL 2 is enabled in the the Docker Desktop app
Verifying that WSL 2 is enabled in the the Docker Desktop app
If you do not have access to a GPU skip the rest of this section and continue to Deploying Eggplant Generator with Docker to install and deploy Eggplant Generator.
Pre-deployment Checklist for Eggplant Generator
Before you deploy Eggplant Generator in your Docker container on Windows, please verify the items on this pre-deployment checklist:
1. Verify the NVIDIA CUDA GPU is Installed and Configured on the Windows System
Verify the NVIDIA CUDA GPU is installed and configured and that you have the necessary drivers installed correctly on the Windows where you plan to run Eggplant Generator in a container.
-
Run the following command to verify the GPU is installed and configured:
nvidia-smi -
Compare the expected output below with the output on your system. The output below (from the command in the previous step) shows a successful GPU installation and configuration.
Mon Jan 20 05:48:32 2025
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| NVIDIA-SMI 553.62 Driver Version: 553.62 CUDA Version: 12.4 |
|-----------------------------------------+------------------------+----------------------+
| GPU Name TCC/WDDM | Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC |
| Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap | Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. |
| | | MIG M. |
|=========================================+========================+======================|
| 0 NVIDIA RTX A2000 WDDM | 00000000:21:00.0 Off | Off |
| 30% 29C P8 4W / 70W | 375MiB / 6138MiB | 0% Default |
| | | N/A |
+-----------------------------------------+------------------------+----------------------+
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Processes: |
| GPU GI CI PID Type Process name GPU Memory |
| ID ID Usage |
|=========================================================================================|
| 0 N/A N/A 8424 C+G C:\Windows\explorer.exe N/A |
| 0 N/A N/A 13548 C+G ...crosoft\Edge\Application\msedge.exe N/A |
| 0 N/A N/A 14320 C+G ...n\132.0.2957.115\msedgewebview2.exe N/A |
| 0 N/A N/A 14780 C+G ...5n1h2txyewy\ShellExperienceHost.exe N/A |
| 0 N/A N/A 16236 C+G ...\Docker\frontend\Docker Desktop.exe N/A |
| 0 N/A N/A 16480 C+G ....Search_cw5n1h2txyewy\SearchApp.exe N/A |
| 0 N/A N/A 17660 C+G ...ekyb3d8bbwe\PhoneExperienceHost.exe N/A |
| 0 N/A N/A 17972 C+G ...n\132.0.2957.115\msedgewebview2.exe N/A |
| 0 N/A N/A 19020 C+G ...CBS_cw5n1h2txyewy\TextInputHost.exe N/A |
| 0 N/A N/A 19660 C+G ....Search_cw5n1h2txyewy\SearchApp.exe N/A |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
2. Verify the NVIDIA CUDA GPU is Installed and Configured in the WSL 2 Container Environment
Verify the NVIDIA CUDA GPU is installed and configured on the system where you plan to run Eggplant Generator on container environments:
-
Run the following command to verify the CUDA GPU is installed and configured:
docker run --rm -it --gpus=all nvcr.io/nvidia/k8s/cuda-sample:nbody nbody -gpu -benchmark -
Compare the expected output below with the output on your system. The output below (from the command in the previous step) shows a successful GPU installation and configuration.
Run "nbody -benchmark [-numbodies=<numBodies>]" to measure performance.
-fullscreen (run n-body simulation in fullscreen mode)
-fp64 (use double precision floating point values for simulation)
-hostmem (stores simulation data in host memory)
-benchmark (run benchmark to measure performance)
-numbodies=<N> (number of bodies (>= 1) to run in simulation)
-device=<d> (where d=0,1,2.... for the CUDA device to use)
-numdevices=<i> (where i=(number of CUDA devices > 0) to use for simulation)
-compare (compares simulation results running once on the default GPU and once on the CPU)
-cpu (run n-body simulation on the CPU)
-tipsy=<file.bin> (load a tipsy model file for simulation)
NOTE: The CUDA Samples are not meant for performance measurements. Results may vary when GPU Boost is enabled.
> Windowed mode
> Simulation data stored in video memory
> Single precision floating point simulation
> 1 Devices used for simulation
GPU Device 0: "Ampere" with compute capability 8.6
> Compute 8.6 CUDA device: [NVIDIA RTX A2000]
26624 bodies, total time for 10 iterations: 31.963 ms
= 221.767 billion interactions per second
= 4435.343 single-precision GFLOP/s at 20 flops per interaction
Next Step: Deploying Eggplant Generator with Docker
After you install and verify your Docker Desktop and NVIDIA GPU CUDA configuration, and complete the pre-deployment checklist, continue to Deploying Eggplant Generator with Docker to install and deploy Eggplant Generator.