With Eggplant DAI, you create models of your systems under test (SUTs) so that Eggplant DAI can use its algorithms to generate tests on your system. Models are composed of states and actions. States are things such as individual screens in an interface. Actions are things that users do in a given screen, or that move users between screens.
When you run a model, the Eggplant DAI engine chooses the path to follow, determining each action based on its algorithm and what steps are possible. To run tests against your SUTs, you link SenseTalk snippets from the Fusion Engine to your actions.
For detailed information about states, see Defining States in Eggplant DAI.
Types of Actions
There are three types of actions in Eggplant DAI:
- Normal: These actions don't need to execute in any particular order relative to other actions. This is the most common action type.
- Sequent: These actions must execute in a specific order relative to certain other actions.
- Previous: These actions return the model to its previous state—that is, the state that caused the transition to the current state.
To change an action's type, select an action, then use the Type drop-down menu in the Action Properties tab to select the desired action type. See Setting Action Properties for more information about action properties.
Linking an Action Back to the Same State
The Previous action type is the only type whose action is predefined specifically to cause a state change. The other action types perform whatever actions are defined in the attached SenseTalk snippets. Therefore, if you want an action to call a new state, the snippet code must explicitly make that happen.
The default behavior of the model is to stay within the same state. A state change occurs only when a state change is called by an action. For example, if the action called was to click a button or enter text in a field in a UI, the action would be performed, then the Eggplant DAI algorithm would choose its next action from within the same state—assuming the action itself didn't cause a state change.
In other words, no action is required (or available) to link an action back to its parent state. All actions remain within their state unless a new state is specifically requested by the attached snippet.
Create Actions
Follow these steps to add an action to a state within your model:
- Select a state. You can select a state on the Model tab by clicking it, or you can select it in the Model tree tab.
- Create an action. There are several ways to do this:
- Click the New Action button
 on the toolbar.
on the toolbar. - Right-click in the selected state, then select New Action from the context menu.
- Use Ctrl+Shift+A.
- Go to Edit Model > New Action.
- Click the New Action button
- After the new action appears in the model, select it, then select the Action Properties tab.
- Configure the action using the guidelines in Setting Action Properties.
Global Actions
Global actions are actions that can execute in any state. A good example of a global action is screen rotation: A user can rotate a mobile device at any time while using your application, so you don't want to limit its execution to any one state.
To add a global action to your model, follow the instructions shown in Creating Actions. However, instead of selecting a state (step 1), make sure that no state or action is selected. When you create an action with nothing selected, the action is a global action.
Setting Action Properties
After creating a new action, you can configure the action properties to customize its behavior. Edit these properties in the Action Properties tab, located in the right pane of the Modeler UI.
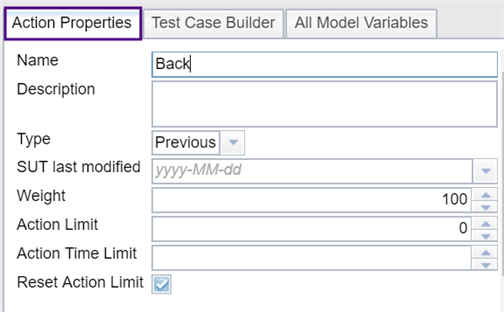
General Properties Section
In the top section of the Action Properties tab, you can adjust the general properties of a action:
- Name: A new action gets created with a default name. Change the name here to something more descriptive for your model. You can use all Unicode (UTF-8) characters but double quotes in this field.
- Description: This field is optional, but you can use it to record any useful information about this action.
-
Type: Use this drop-down list to set the action type. New actions are created with the type Normal, which is typically what you will use for most actions. However, you can switch to Sequent or Previous here if required. See the Types of Actions section above for a description of each action type.
- SUT last modified: Use this drop-down list to set the last modified date for the SUT. When calculating which action to execute next, Eggplant DAI will consider only coverage obtained after the SUT last modified date.
- Weight: This setting lets you change the probability of an action being executed when the model runs. The default weight for an action is 100. If you change that value to 50, the action is half as likely to be executed as an action with the weight value of 100.
- Action limit: This value sets an upper boundary for the number of times an action can be performed during a test run. Use this setting along with the Reset action limit checkbox to manage the number of times an action can run during a visit to a state or during the whole test run.Note: New actions have the default action limit value of 0 (zero). This value means there is no limit on the number of times the action can be visited.
- Action time limit: This value sets an upper limit for the amount of time (in seconds) it takes for an action to execute. This setting is useful for performance testing. The default value is 0.
- Reset action limit: This checkbox determines whether the Action limit setting applies to single visits within a state or to the entire test run:
- When selected, Eggplant DAI resets the action's test count each time it exits a state so that the limit applies to the number of times this action can execute per visit to the state.
- When cleared, Eggplant DAI counts the action's occurrence across the test run. In this case, the Action limit determines the number of times this action can execute during the whole test run.
Connections from Action Section
Use this section to configure an action to connect to a state. The left side of this table is for Connection Selection, and it includes three columns:
- State: This column lists all the states in the model.
- Connection
 : Use this checkbox to create a connection between the state and the action selected in the model.
: Use this checkbox to create a connection between the state and the action selected in the model. - Visibility
 : Select this checkbox for a connection if you don't want the arrow to appear on the model. If your model is complex, with many connected actions and states, using this option can simplify your view. With this selection, the connected state is shown as a shadow box under the originating action:
: Select this checkbox for a connection if you don't want the arrow to appear on the model. If your model is complex, with many connected actions and states, using this option can simplify your view. With this selection, the connected state is shown as a shadow box under the originating action: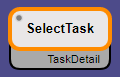
In the example above, the SelectTask action connects to the TaskDetail state.
The Condition for Connection section on right side of the table is where you can set conditions that must be met before an action can connect to a state. This section includes three columns:
- Parameter: Select a variable from the drop-down list to use to set a condition.
- Condition: Select the comparison method (i.e., <, >, ==) from the drop-down menu that the variable must meet before the action connects to a state.
- Value: Set the value to evaluate against the variable.
Snippets Called by Action Section
This section lists any snippets that you have linked to the selected action. A snippet is a specific piece of SenseTalk code that executes when this action is encountered during a test run.

The Snippets called by action section of the Action Properties tab
You can add snippets to states or actions by using the Model and Snippets tabs. For information about linking snippets this way, see Linking Models to Snippets.
If you know the name of a snippet you want to attach to an action, you can add it here. Click in the Name field, then enter the snippet name.
Action Variables Section
Action variables capture and provide values for states and actions. To add a variable to an action, right-click the action, then select New Variable in the drop-down menu. You can also select an action, then click New in Action variables, located in the right pane.
The Action Variables section of the Action Properties tab
To set the properties for generating a variable, right-click the variable, select Edit variable details in the context menu, then use the Variable properties dialog box to set the criteria.
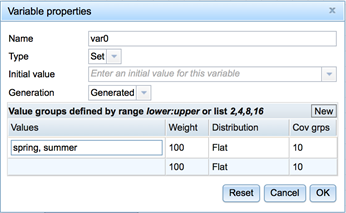
- Name the variable. You can use all Unicode characters but double quotes in this field.
-
Select a variable Type:
- Integer: This selection defines a variable as a whole number (not a fraction) that can be positive, negative, or zero. Use the integer variable type in models when, for instance, a count of something is important, such as the number of users or test cases.
- True or False: Use this type when your model requires a Boolean value, such as on or off, true or false, or similar values.
- Real: The real data type includes rational numbers, such as 5, -5, and 2/3. It also includes irrational numbers, such as the square root of 2. Use a real data type for values such as for degrees, radians, or other similar information.
- Text: Use this data type to store a string. You can also use the Text data type to define an allowable list of characters as a string. You can use all Unicode characters but double quotes in this field.
- Set: This selection lets you define a set of allowed values for this variable. Use this selection if you want Eggplant DAI to select a value from a specific list of values at runtime. For example: 'spring', 'summer', 'autumn', 'winter’. To input your list of values, right-click the variable, select Edit Variable Details from the context menu, then use the Values section of the Variable Properties dialog box to set the values. You can use all Unicode characters but double quotes in this field.
- Record: This selection lets Eggplant DAI read variable values from records contained in a CSV file. Go to File > Manage Execution Environments to identify the directory containing the CSV files. When Eggplant DAI accesses this variable, it selects one of the records from the CSV file and stores it in the variable.
Note: When using data from a CSV file to pass values to a variable, if a row of the CSV file contains four comma separated values (e.g., "spring, summer, autumn, winter"), then the whole row will be passed to the variable. If you only require a specific value from the list, e.g., "autumn", then you must parse it using a snippet in Eggplant Functional.
- Set the Initial value of the variable. When using variables of the type Record, the option you select in the Initial value field will determine the .csv file from where the records should be read from.
-
Set the Generation method you want Eggplant DAI to use:
- Generated: Generates a new value for a variable based on its variable type.
- Generated Unique: Generates a value, but can't reuse a value that has been previously used.
- Generated one-time: The generated value is selected once and then not selected again. The value remains static throughout the run.
- Non-generated: The value is not generated and must be set to contain a value.
-
You can add Value groups to further define the variables Eggplant DAI generates. Enter a value group as a value definition, using one definition per line.
-
Values: Enter the allowable values for this group entry. You can define variable values as follows:
- Enter a static value, such as 100.
- Enter a range, such as 0:100.
- Enter a list, such as 0, 2, 4, 6, 8.
- Weight: Enter the relative weight you want Eggplant DAI to use when generating this variable. For example, if you want Eggplant DAI to use this value group 50 percent of the time (as compared to the other value groups) when generating this variable, enter 50 in this field.
-
Distribution: Select the statistical distribution method you want Eggplant DAI to use when generating this variable:
- Flat: Use a flat statistical distribution model.
- Normal: Use a normal statistical distribution model.
- Edge: Use statistical outliers.
- Cov grps: Determines the number of segments Eggplant DAI uses to divide the values entries. Eggplant DAI begins with a value of 10 equal segments by default, then processes the values you enter for a value group and suggests a coverage group. For example, if you enter 0:360, as a value, Eggplant DAI might suggest 10 coverage groups that include 36 possible values for each coverage group to cover the value range from 0 to 360. You can manually enter a coverage group value that meets the needs for your model.
-
Associated Tags Section
Tags identify specific properties about a model. You can create and apply these tags to actions to track those properties within that model.
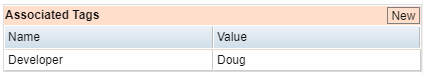
The Associated Tags section of the Action Properties tab
Use the settings in this section to associate tags with the actions in your model. See Using Tags in Eggplant DAI for information about creating tags, then applying the tags you create to an action within a model.
Preconditions for This Action to Execute Section
You might want a model execution to call an action only after a specific condition has been met. For example, a button might be disabled until data is entered in a field. To model this case, you would create actions that are enabled based on variable values.
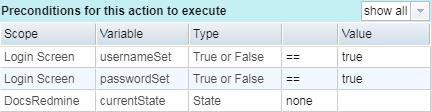
The Preconditions for This Action to Execute section of the Action Properties tab
Use this section to set evaluation criteria for preconditions. The Preconditions section lists each defined state variable for the parent state of the selected action, along with any global variables.
Tip: The currentState variable is a special predefined global variable that contains the name of the current state. You can use this variable to prevent a global action from being called from a specific state. For instance, if you have a global action for Quit, you might want to block that action from being called from your Initial state.
The table in this section displays the following information:
- Scope: The state or model in which the variable is set.
- Variable: The variable name.
- Type: The variable type (e.g., True or False, Integer, Text).
- Condition: An evaluation method you want to apply against the variable value (e.g., ==, >, <). Select the appropriate method from the drop-down list to set a precondition.
- Value: The value to evaluate a variable against. Enter the value in this field to set a precondition.
For more information about preconditions, see Setting Preconditions for Actions.
Set and Generate Variable Values Section
Use this section to set or generate variable values when a given action is performed. When an Eggplant DAI model execution performs the selected action, you can change values for the variables listed in this section. The table displays all state variables for the parent state of the selected action as well as all global variables.
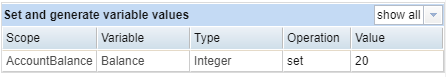
The Set and Generate Variable Values section of the Action Properties tab
The table in this section displays the following information:
- Scope: The state or model in which the variable is set.
- Variable: The variable name.
- Type: The variable type (e.g., True or False, Integer, Text).
- Operation: Use this drop-down list to determine whether a variable value is changed when the action is encountered by the model. Your choices are:
- none: (Default) The variable value is not changed.
- set: Select this option if you want to set a specific value.
- generate: Select this value if you want to generate a new value for the variable.
- Value: Use this drop-down menu to select a value if you choose to set a new value in the Operation field. Your choices are determined by the type of variable.
Checks to Perform in Action Section
Use this section to test the value of a variable, and to display a message based on the outcome of that test when the action executes.
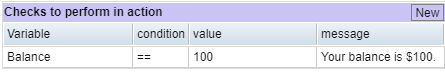
The Checks to Perform in Action section of the Action Properties tab
First select an action. Then you can set up the checks:
- Choose the Variable for which you want to test a condition.
- In the Condition column, select a evaluation condition (e.g., <, >) that you want Eggplant DAI to use to test the variable's value.
- Set a Value against which you want the variable value evaluated.
- Enter the Message you want Eggplant DAI to display if the condition is met.
It's possible to build more complex tests using variables. For example, you might add variables to an action that capture responses from your SenseTalk snippets, then use these responses to create additional variables and pass them to other snippets or actions.
Actions and Performance Testing
Setting an Action time limit in the Action Properties tab makes it possible to track performance using Eggplant DAI.
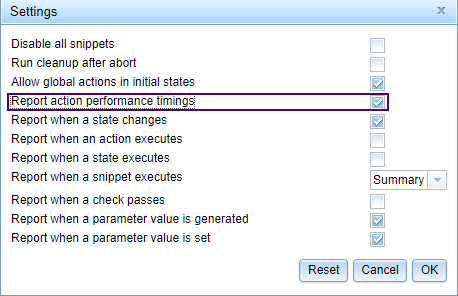
To see action time results in reports, enable that capability in the Settings tab.
- Go to File > Settings.
- Select the Report action performance timings checkbox.
- Click OK.
Action timing results display in the console as the test runs:
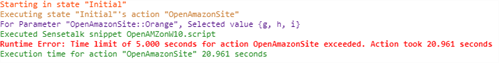
The log shown above displays an error because an action took more time to execute than the set action time limit.