With Eggplant AI, you create models of your systems under test (SUTs) so that Eggplant AI can use its algorithms to generate tests on your system. Models are composed of states and actions. States generally represent the screens within a software application. Actions are the user actions that can be performed within a state, including actions that move users between states.
Below you will find information about creating and using states in Eggplant AI models. For information about actions, see Creating Actions in Eggplant AI.
Types of States
Eggplant AI states can be one of four types:
- Start: This state type is used for the initial state, or starting point, for your model.
- Exception: This state type is used for the Error state that is added automatically when you create a new model. You can use this state for error handling.
- Cleanup: This state type is used for the Cleanup state that is added automatically when you create a new model. You can use this state for any cleanup steps you want to perform on your SUT at the end of model runs.
- Normal: This state type is used for all other states. Most of your model will be built with the Normal state type.
Default States in a New Model
When you create a new model in Eggplant AI, the green Start state is placed in the Model tab workspace automatically with a name of Initial. You can select the State Properties tab in the right pane, then change the state's Name to something that better represents your model.
If you click the Model tree tab in the left pane, you see that the new model has the following states by default:
- Initial: This is the Start state, the starting point for model runs.
- Error: This state has the type Exception. Eggplant AI calls this state whenever an error occurs when running a model. An error can occur when a model check fails or when a problem occurs within a SenseTalk snippet. To use error handling in these situations, you need to attach an appropriate SenseTalk snippet to this state. If no snippet is attached when this state is called, the model run exits without taking any action here.
- Cleanup: Eggplant AI calls this state just before a model run exits. You can use the Cleanup state to tidy up the SUT prior to exiting, if necessary, by attaching an appropriate SenseTalk snippet. For example, you might need to close applications or database connections. If no snippet is attached when this state is called, the model run exits without taking any action here.
- Exit: This state does not contain any actions. When Eggplant AI calls this state, the model run ends.
Typically, only the Start state and any Normal states you add display on the Model tab workspace. The Exception, Cleanup, and Exit states appear only in the Model tree tab.
Creating Model States
To create a new state, do one of the following with the Model tab selected:
- Click the New State button
 on the toolbar.
on the toolbar. - Right-click within the Model tab workspace, then select New State from the context menu.
- Select Edit model > New State from the main menu.
- Use Ctrl+Shift+S.
With a state selected, you can change the state's name and other properties in the State Properties tab in the right pane.
After adding states to the model, follow the instructions in Creating Actions in Eggplant AI to add actions to your model.
Setting State Properties
To customize the behavior of your model, you can adjust the properties associated with states. To modify a state's properties, select the state in the Model tab, then select the State Properties tab in the right pane.
The State Properties tab provides access to all the state's properties. You can set these properties when you first create states for your model, and you can return here later to adjust properties as necessary.
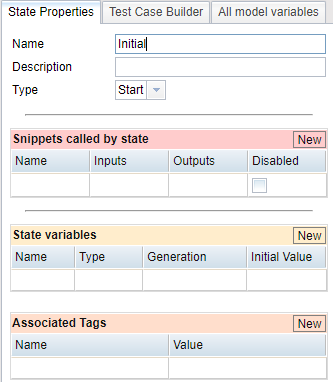
The State Properties tab in Eggplant AI
General Properties Section
In the top section of the State Properties tab, you can adjust the general properties of a state:
- Name: A new state gets created with a default name. Change the name here to something more descriptive for your model. You can use all Unicode (UTF-8) characters but double quotes in this field.
- Description: This field is optional, but you can use it to record any useful information about this state.
- Type: Use this field to change the state type. The available state types are described in Types of States.
Note: Typically, you won't need to adjust the state type. New states are created with the Normal type by default, which is what most of your model is composed of. You should not have more than one each of the Start, Exception, and Cleanup state types per model.
Snippets Called by State Section
This section lists any snippets that you have linked to the selected state. These are the snippets that execute when this state is encountered during a model run. A snippet is a specific piece of SenseTalk code that interacts with the SUT when the model calls a state or action.
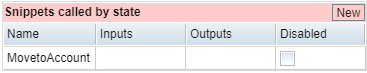
The Snippets called by state section of the State Properties tab
You can add snippets to states or actions by using the Model and Snippets tabs. For information about linking snippets this way, see Linking Eggplant AI Models to Snippets.
However, if you know the name of a snippet you want to attach to a state, you can add it here. Click in the Name field, then enter the snippet name.
State Variables Section
Use the settings in this section to configure variables you want to use in this state and within snippets called by this state. A state variable can be used by a state or an action within a state. It also can be passed in and out of a snippet.
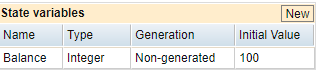
To add a new variable, click New in the State variables section. You can also select then right-click the state in the Model tab, then select New Variable from the context menu. You can configure state variables by using the selections shown here:
- Name: Enter an appropriate name for your variable. You can use all Unicode characters but double quotes in this field.
-
Type: Enter the appropriate variable type from the drop-down menu:
- Integer: This selection defines a variable as a whole number (not a fraction) that can be positive, negative, or zero. Use the integer variable type in models when, for instance, a count of something is important, such as the number of users or test cases.
- True or False: Use this data type when your model requires a Boolean value such as on or off, true or false, and other similar values.
- Real: The real data type includes rational numbers, such as 5, -5, and 2/3. It also includes irrational numbers, such as the square root of 2. Use a real data type for values such as for degrees, radians, or other similar information.
- Text: Use this data type for storing a string or to define an allowable list of characters as a string. It can be any integer constraint, i.e., 2, 4, 8, 16 would make a string of either 2, 4, 8, or 16 characters long and much like other constraints, you can combine multiple constraints here. If you want to set a range of allowable characters, you must make them a range, e.g., 'a':'z' or a list "aeiou". Remember that the single and double quotes are important.
- Set: This selection lets you define a set of allowed values for this variable. Use this selection if you want Eggplant AI to select a value from a specific list of values at runtime. For example: 'spring', 'summer', 'autumn', 'winter’. To input your list of values, right-click the variable, select Edit Variable Details from the context menu, then use the Values section of the Variable Properties dialog box to set the values. You can use all Unicode characters but double quotes in this field.
- Record: This selection lets Eggplant AI read variable values from records contained in a CSV file. Go to File > Manage Execution Environments to identify the directory containing the CSV files. When Eggplant AI accesses this variable, it selects one of the records from the CSV file and stores it in the variable.
-
Generation: Enter the appropriate variable generation method from the drop-down menu:
- Generated: Generates a new value for a variable based on its variable type.
- Generated Unique: Generates a value, but can't reuse a value that has been previously used.
- Generated one-time: The generated value is selected once and then not selected again. The value remains static throughout the run.
- Non-generated: The value is not generated and must be set to contain a value.
- Initial Value: Set the initial value, if any, for this variable. When using variables of the type Record, the option you select in the Initial value field will determine the .csv file from where the records should be read from.
To edit an existing variable, select it and update the information in the State variables section. To further customize variables, right-click the variable, then select Edit Variable Details. The Variable Properties dialog box lets you set an initial value as well as value ranges and other details.
To remove a variable, right-click the variable in the State Variables section, then select Remove Variable from the context menu.
Associated Tags Section
Eggplant AI lets you create tags to identify specific properties about a model. You can apply these tags to states to track those properties within the model. Use the settings in this section to associate tags with the states in your model. See Using Tags in Eggplant AI for information about creating tags, then applying the tags you create to a state within a model.