JMX Monitor
This monitor uses Java Management Extensions (JMX) to collect measurements from remote Java applications, devices, and service-driven networks.
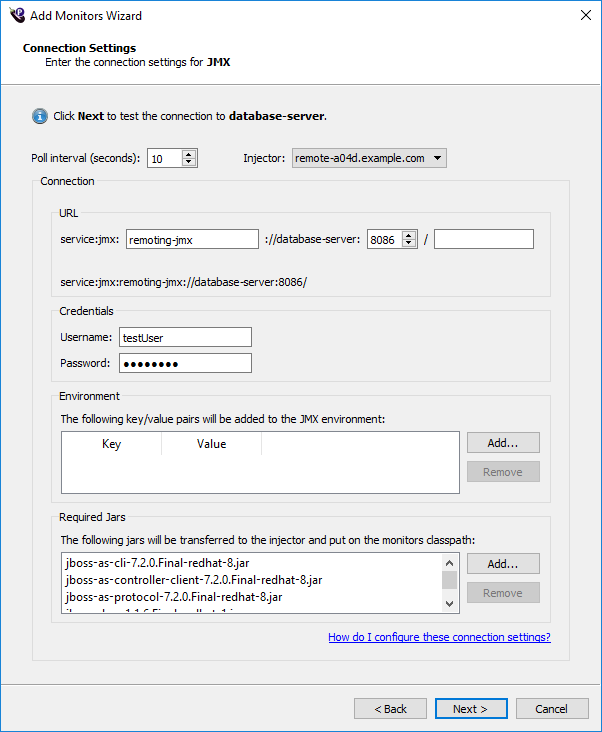
For information about the Poll Interval and Injector fields, refer to Connection settings.
Connection URL and credentials
Connections using JMX require a URL, username, and password. Different Java applications use different connection URLs.
For example:
To connect to Tomcat, use a URL of the form:
service:jmx:rmi:///jndi/rmi://monitoringTargetHostname:port/jmxrmi
To connect to JBOSS, use a URL of the form:
service:jmx:iiop://monitoringTargetHostname:port/jndi/JMXRemote
You might need to open the specified TCP port on any firewalls between the injector machine and the monitoring target.
JMX Environment
Some Java applications (such as Oracle WebLogic) require key/value pairs to be set in the JMX environment. Specify these key/value pairs in the Environment list by using the Add and Remove buttons. For example, setting jmx.remote.protocol.provider.pkgs to the value weblogic.management.remote is equivalent to the following code:
env.put(JMXConnectorFactory.PROTOCOL_PROVIDER_PACKAGES, "weblogic.management.remote");
Required Jars
Some Java applications (such as JBOSS) require certain .jar files to be present on the classpath of the monitor. Specify these .jar files in the Required Jars list by using the Add and Remove buttons.
When you select a .jar file, it will be copied into the jmxJars/ folder in your workspace. When you run a test, the .jar file will be copied to the File transfer repository (usually C:/fcCache) on the injector machine. These copies are not deleted after the test, so it is your responsibility to remove unused .jar files.