Linux Monitor
The Linux monitor uses a variety of commands (such as sar and iostat) over SSH or telnet to collect measurements from a monitoring target running Linux.
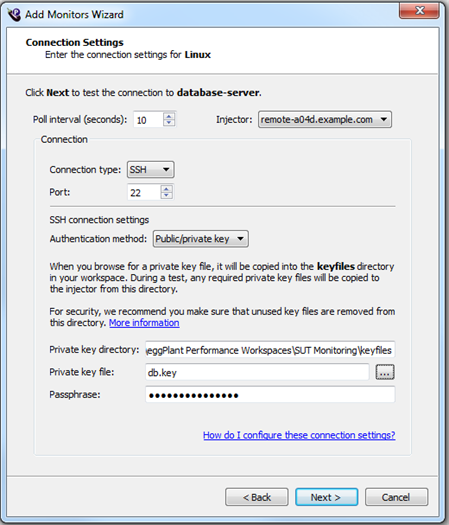
For information about the Poll Interval and Injector fields, refer to Connection settings.
Whichever connection method is used, the user account must have permission to run the Linux commands: vmstat, free, iostat, sar and df. Depending on the measurements collected during the test, multiple telnet or SSH sessions might be opened with the same user account.
You might need to open TCP port 22 or 23 on any firewalls between the injector machine and the monitoring target.
There are three options for configuring a connection to a monitoring target running Linux:
Connection using Telnet
Specify a TCP port for connecting to telnet on the monitoring target. The default port is 23.
Specify a username and password.
Connection using SSH and password
Specify a TCP port for connecting to ssh on the monitoring target. The default port is 22.
Specify a username and password.
Be aware that if you are trying to monitor a Linux AWS instance, AWS EC2 disables SSH password authentication by default. Configure it manually, or use the private key file method described below.
Connection using SSH and Private Key File
Specify a TCP port for connecting to ssh on the monitoring target. The default port is 22.
To connect using SSH, you can provide a private key file. This is a file generated by a program such as ssh-keygen or PuTTYgen. The private key resides on the computer from which the connection is made. It should have a public key counterpart which is stored in ~/.ssh/authorized_keys on the remote computer (the monitoring target).
If the private key file is protected with a passphrase, enter it into the Passphrase box. Otherwise leave it blank.
When you select a private key file, it will be copied into the keyfiles folder in your workspace. When you run a test, the private key file will be copied to the File transfer repository (usually C:/fcCache) on the injector machine. These copies are not deleted after the test, so it is your responsibility to remove unused private key files to protect the security of the system under test.