Configuring a Mail Server in Eggplant Functional
Eggplant Functional (EPF) can send emails as notifications of test results. Email notifications let interested parties quickly learn the outcomes of test executions and react as needed. Eggplant Functional uses the SendMail command to send emails, so these email notifications are controlled at the script level.
Configuring SMTP Settings
You must have an account with an SMTP server provided by your organization or by a third party, such as Gmail. It is often helpful to consult the administrator of the SMTP server to get a good idea of which settings are relevant to your specific SMTP server. Some trial and error, experimenting with different combinations of settings, is required when the SMTP server details are unknown.
Eggplant does not provide you with an SMTP server.
Eggplant Functional takes the SMTP server properties you provide and attempts to send an email using those settings, and displays errors if it is unable to send an email using those properties. Eggplant Functional errors in Windows are generic and indicate that Eggplant Functional is unable to send an email with the provided SMTP properties. In Mac OS, view the generic error in the Console for additional information about the nature of the error.
It is possible to specify SMTP mail server properties at either the script or application level.
When using SendMail in an Eggplant Functional script that is run via command line, such as through Eggplant Manager, Jenkins, HP ALM, etc., it is generally necessary to provide all of the required mail server properties inline with the SendMail command. This is because the instance of Eggplant Functional is usually running as a user that does not have access to application-level preferences. Script-level configuration is achieved by including the smtp_host, smtp_type, smtp_user, smtp_password, and smtp_port properties and their associated values as part of the SendMail command.
To quickly test whether your application-level SMTP properties are correct, write a simple SendMail command that includes the necessary properties for your SMTP mail server, and execute the command in Eggplant Functional. If Eggplant Functional reports that the email was sent, and you receive the test email, your configuration is correct.
Example:
sendMail (To:"tester@testing.com", from:"tester@testing.com", smtp_host:"<smtp mail server IP or hostname>",smtp_type:"login", smtp_user:"tester", smtp_password:"123456", smtp_port:"465" ,Subject:"test email")
If you plan to consistently use the same SMTP server for all emails sent from Eggplant Functional and will only run the scripts through the Eggplant Functional GUI, you can configure SMTP server information at the application level to simplify your code.
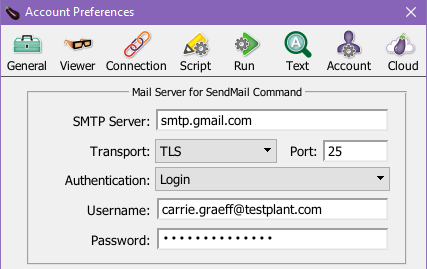
To configure SMTP server settings for the entire Eggplant Functional Preferences, go to Eggplant > Preferences > Accounts. Provide an SMTP Server ID, Transport type, Port number, and Authentication type. Most, but not all, SMTP servers require a User Name and Password, so provide these details when applicable.
Example:
sendMail (To:"test@gmail.com", Subject:"Test email worked!")
Below is an example of correct configuration for Gmail within Eggplant Functional preferences.
Setting up Email Notifications
Because email notifications from Eggplant Functional are controlled by the SendMail command, you can choose if and when email notifications are sent during a script execution. For example, email notifications might only be of interest when a script fails, or when a particular UI element appears on the system under test. You could also set a SendMail command to run after every execution, using the Settings pane in the Eggplant Functional Suite.
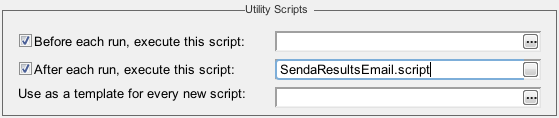
The SendMail command is able to attach files, such as Eggplant Functional log files and screenshots, to the email.
Below is a SenseTalk example that sends an email each time a script finishes execution and sets an appropriate attachment and title depending on the outcome of the execution.
Example:
set TestList to ("script1","script2","script3") -- create a list of the scripts you want to run, in the order in which you'd like to run them
//repeat this process with each script in the list
repeat with each item TestScript of TestList
RunWithNewResults TestScript -- run each script in the test, creating a new set of results for each
put the result into Outcome -- get the result of the script execution and store it in a variable
put TestScript & the long date into title -- create the title for the email
put Outcome's logfile into screenError -- store the file path of the log file
replace "logfile.txt" with "screen_error.tiff" in screenError -- store the file path of the screen error, if there is one
// Use a conditional statement to send the email based on whether or not the script failed
if Outcome's status is "failure"
then
SendMail(To: "someone@somecompany.com",\
subject:title,\
body:"the test script generated an error.",\
attachment:(screenError, Outcome's Logfile)) -- Indicate the attachments. Note, this will log a warning in your master script log file if there is no screen error to attach.
else
// send an email with the log file attached
SendMail(to: "firstname.lastname@somecompany.com",\
subject: title,\
body: "the test script ran successfully.",\
attachment: Outcome's logfile)
end if
end repeat
Troubleshooting and Special Considerations
Eggplant Functional must be able to talk to your mail server. Not all mail servers are able to communicate with an SMTP client, however, and some networks are configured to block such communication between an SMTP client and mail server.
Every mail server and network is configured differently, so consult your IT department or system administrator if you are unsure of the SMTP mail server properties that are needed to communicate with your mail server.
For example, if you are using a Microsoft Exchange mail server, the mail server must be configured for SMTP, which is disabled by default, and if you are using Gmail's SMTP mail server, you must disable 2-step verification, and to allow access by less secure apps.