Eggplant Functionalで初めてのSUT接続を作成する
EPF でテストを開始する最も簡単な方法は、Windows マシンを"Single System モデル"で Eggplant ホスト マシンと SUT の両方として設定することです。これは、Eggplant Functional の使用開始 ページで説明されている Eggplant の設定です。
Single System モデルはよりシンプルな構成ですが、Eggplant Functional による自動テストは 2 システム モデルで動作するように設計されています。つまり、Eggplant Functional は 1 台のコンピュータで実行され、テスト対象のシステムまたはアプリケーションがある任意の数の他のコンピュータまたはデバイスに接続できます。2 システム モデルのシステムは次のとおりです。
-
Eggplant マシン: ("Eggplant コントローラ マシン"と呼ばれることもあります) Eggplant Functional (EPF) をインストールして実行するシステム。Eggplant マシンには、スクリプトや関連イメージなど、テストを実行するために必要なものがすべて揃っています。Eggplant Functional を実行できるシステムの詳細については、前提条件 ページを参照してください。
-
テスト対象システム (SUT): テストするアプリケーションが実行される 2 番目のシステム。SUT には、デスクトップ マシン、仮想マシン、モバイル デバイス、さらには POS (販売時点管理) システムや HMI (ヒューマン マシン インターフェイス) システムなど、さまざまなシステムが含まれます。使用できるその他の種類の SUT の詳細については、SUT への接続を参照してください。SUT の前提条件の詳細については、テスト対象システム (SUT) の推奨事項と要件を参照してください。
最初の SUT を設定する手順は次のとおりです。
-
Windows 上で EPF を実行している場合は、以下の Windows での最初の SUT 接続 で説明されているように、Single System モデルを使用して開始できます。
-
次の手順では、EPF が SUT とは別のマシンで実行される 2 システム モデルで Mac または Linux 上で EPF を実行する方法について説明します。 Windows SUT への VNC 接続と RDP 接続を作成する方法を説明します。これら 2 つの接続タイプの詳細については、Eggplant Functional 接続タイプ: VNC と RDP を参照してください。
接続リストの使用
EPF には、接続を表示および管理するための接続リスト ウィンドウが用意されています。Connection List では、接続を作成および編集します。最初の接続を作成して保存すると、Connection List でその接続を確認し、SUT に接続されているかどうかなどの情報を表示できます。Connection List の使用方法の詳細については、Connection List を参照してください。
Connection Listを開くには、Eggplant Functionalを起動し、Eggplant FunctionalのメインメニューからConnection > Connection Listを選択します。
Connection Listを使用して接続を作成して保存す�ると、その接続は Eggplant の設定に保存されます。削除するまで、Connection Listに残ります。この方法で作成した接続は、"保存済み"または"永続的"な接続と呼ばれます。EPF を終了して再起動した後も、接続は保持されます。
EPF は"一時"接続もサポートします。一時接続とは、スクリプトの実行中に SenseTalk の connect コマンドを使用して作成する接続です。これらの接続は設定に保存されず、EPF を終了して再起動すると保持されません。connect コマンドの使用法については、接続コマンド を参照してください。
Windows での最初の接続
EPF でテストを開始する最も簡単な方法は、Windows マシンを"Single System モデル"で Eggplant ホスト マシンと SUT の両方として設定することです。これは、Eggplant Functional の使用開始 ページで説明されている Eggplant の設定です。
ステップバイステップ: Single Systemの接続詳細の入力
前述のように、このよりシンプルなSingle Systemのセットアップについては、[Getting Started](epf-getting-started-eggplant- functional.md) ページの [Step by Step: Setting Up Eggplant Functional](epf-getting-started-eggplant- functional.md#step-by-step-setting-up-eggplant- functional) で説明されています。
Windows での最初の接続
次の手順では、2 システム モデルの Mac または Linux で Eggplant Functional を実行する方法について説明します。Eggplant Functional は SUT とは別のマシンで実行されます。 Windows SUT への VNC 接続および RDP 接続を作成する方法を示します。これら 2 つの接続タイプの詳細については、Eggplant Functional Connection Types: VNC vs. RDP を参照してください。
以下の手順は、Mac または Linux に EPF がすでにインストールされていることを前提としています。EPF をまだインストールしていない場合のインストール方法については、[Eggplant Functional のインストール](epf-installing-eggplant- functional.md) を参照してください。
Eggplant マシンと SUT システムをセットアップしたら、Eggplant Functional の Connection List を使用してそれらの間に接続を作成し、自動テストを開始できます。以下の手順に従って、最初の SUT 接続を作成します。
ステップバイステップ:VNC接続の追加
-
UltraVNC などの VNC サーバーを SUT にインストールして実行します。ユーザー�名とパスワードを要求するように VNC サーバーを構成する場合は、EPF の VNC 接続でそのユーザー名とパスワードを入力する必要があることに注意してください。
-
Eggplant マシンの EPF で、メイン メニューから Connection > Connection List に移動して接続リストを開きます。接続が追加されていない場合、接続リストは次のサンプル ウィンドウのようになります。
-
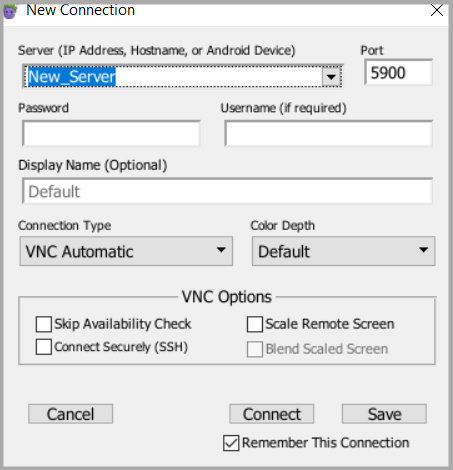
Add をクリックして、New Connection パネルを開きます。接続リスト ウィンドウの下部または Add a connection セクションにある Add ボタンを使用できます。New Connection パネルが開くと、Connection Type ドロップダウン メニューでデフォルトで VNC Automatic が選択されていることがわかります。この設定は、ほとんどの VNC 接続に適しています。
-
SUTのIPアドレスまたはホスト名を**サーバー(IPアドレス、ホスト名、またはAndroidデバイス)**フィールドに入力します。VNC接続では、ポートはデフォルトで5900に設定されています。必要に応じて、Portフィールドの値を変更できます。
-
必要に応じて、PasswordとUsernameを入力します。VNC接続の場合、これらのフィールドは、SUTのVNCサーバーの値を指します。
-
Display Name フィールドに接続の名前を入力します。このフィールドはオプションですが、接続を識別するための説明テキストがあると便利です。表示名を入力しない場合は、Server フィールドの値が接続リストの名前として使用されます。
先端Connectコマンドで SenseTalk スクリプトの表示名を使用して、特定の接続を開き、定義した接続の詳細を活用します。したがって、ベスト プラクティスとして、表示名を短くして覚えやすいものにすることを検討してください。 -
Save をクリックして、接続の詳細を接続リストに保存します。保存する前に他の接続オプションを設定または変更できますが、最初の接続ではデフォルト設定で問題ありません。
接続リストに新しい接続が追加され、リストまたはテーブルとして表示されるようになります:
新しく作成した VNC 接続を使用するには、SUT への接続に進みます。
ステップバイステップ:RDP接続の追加
-
SUT マシンでリモート アクセスを有効にします。たとえば、Windows でリモート デスクトップを有効にします。
-
Eggplant マシンの EPF で、メイン メニューから Connection > Connection List に移動して接続リストを開きます。接続リストに接続を追加していない場合、ウィンドウは次のサンプル ウィンドウのようになります。

-
Add をクリックして、New Connection パネルを開きます。ウィンドウの下部または Add a connection セクションにある Add ボタンを使用できます。
-
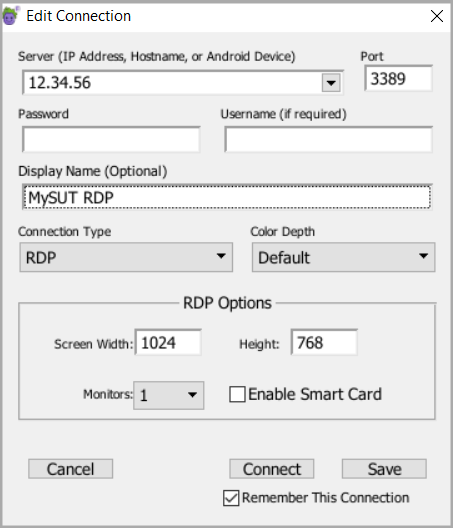
Connection Typeドロップダウンメニューで、RDPを選択してRDP接続を作成します。
-
SUTのIPアドレスまたはホスト名を**サーバー(IPアドレス、ホスト名、またはAndroidデバイス)**フィールドに入力します。RDP接続では、ポートはデフォルトで3389に設定されています。必要に応じて、Portフィールドの値を変更できます。
-
PasswordとUsernameを入力します。RDP接続では、この情報は接続先のSUTのWindowsユーザーアカウントを指します。この情報は、RDP接続では常に必要です。
-
Display Name フィールドに接続の名前を入力します。このフィールドはオプションですが、接続を識別するための説明テキストがあると便利です。表示名を入力しない場合は、Server フィールドの値が接続リストの名前として使用されます。
先端表示名は、
ConnectコマンドでSenseTalkスクリプトを使用して、特markdown 定の接続を開いたり、定義済みの接続詳細を活用したりできます。そのた��め、ベストプラクティスとして、表示名を短く覚えやすいものにしておくことを検討してください。 -
Save をクリックして、接続の詳細を接続リストに保存します。保存する前に他の接続オプションを設定または変更できますが、最初の接続ではデフォルト設定で問題ありません。
接続リストに新しい接続が追加され、リストまたはテーブルとして表示されるようになります:
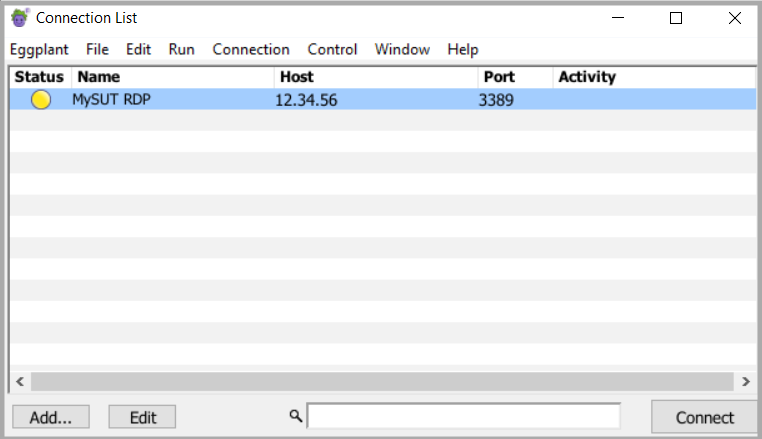
新しく作成した VNC 接続を使用するには、SUT への接続に進みます。
SUTへの接続
接続リストで接続を定義した後、このウィンドウからそれらの SUT に接続することもできます。
接続を開くには、次のことができます。
- リストで接続を選択し、Connectをクリックする
- リストの接続をダブルクリックする
Eggplant Functional が接続を確立している間、Activity 列が進行状況を示す情報で更新され、Status 列の色付きのドットも変化します。
接続が確立されると、EPF ビューアー ウィンドウが開き、次に示すように SUT デスクトップが表示されます。
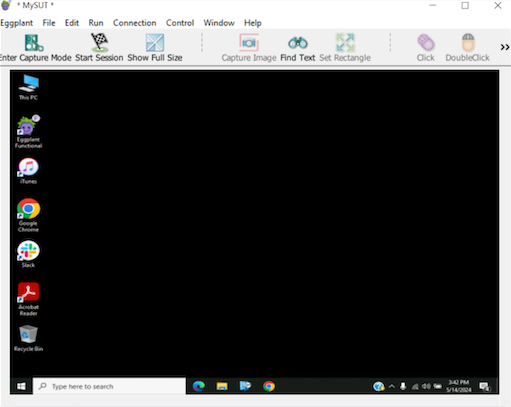
これでテストを開始する準備ができました。
SenseTalk の Connect コマンドを接続の表示名とともに使用して、SUT に定義された詳細を利用することもできます。次のコード行は、上で定義した RDP SUT に接続する方法を示しています。
Connect "Windows2RDP"
このコマンドの使用方法の詳細については、Connectコマンドを参照してください。